Which Best Describes Absorption in the Small Intestine
Absorption of Digested Food. A nutrient-coupled Na absorption mediated by several families of Na -dependent nutrient transporters such as sugar or amino acid transporters discussed separately in this chapter b electroneutral NaCl absorption mediated primarily via the Na H exchange mechanism and c colon.
Absorption In The Small Intestine
Nephrons filter the blood in the small intestine before the nutrients are transported to other tissues.
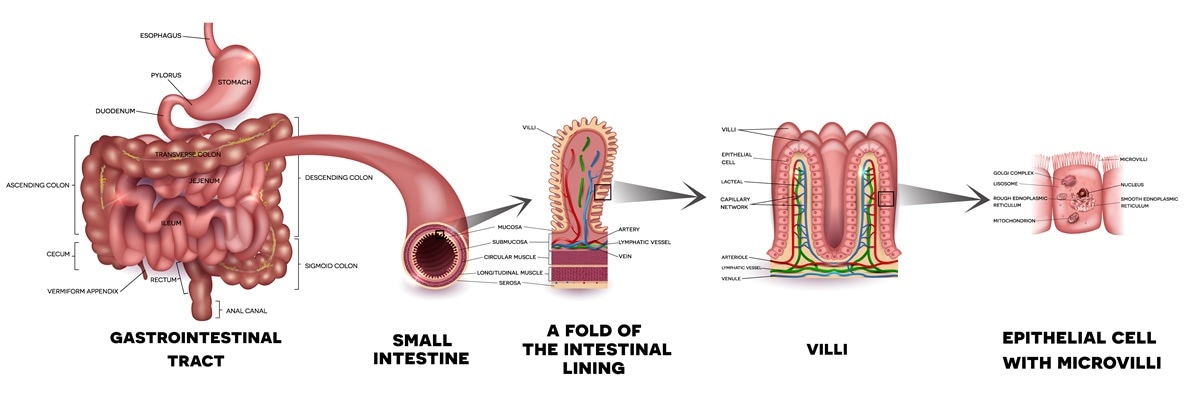
. Three mechanisms contribute to the apical Na transport in the small intestine. Which Definition best describes absorption. Blood transports nutrients from the small intestine to other body tissues.
The Small intestine is a coiled hollow tube that extends from the stomach to the large intestine. Copper is absorbed in the proximal small intestine and stomach. Which statement best describes the process of absorption.
The primary function of the small intestine is the absorption of nutrients and minerals found in food. The selective intake and chemical breakdown of food in the body. Longest component of the GI tract.
Absorption occurs by a saturable active transport process at lower levels of dietary copper and by passive diffusion at high levels of dietary copper. In the stomach the enzyme pepsin acts on the peptide bonds of the protein and break it down into the smaller proteins. The food enters into the small intestine from the stomach in which the digestion of proteins begins.
The breakdown of food into a form usable by the body C. Important Notes For NEET Biology Digestion and Absorption. Simple diffusion facilitated diffusion osmosis active transport.
Food is broken down into individual nutrients and molecules. The Small Intestine. The thin surface layer.
The small intestine is the part of the gastrointestinal tract between the stomach and the large intestine where much of the digestion of food takes place. Simple diffusion Facilitated diffusion Active Transport and Pinocytosis The small intestine is to nutrient absorption as. Four methods of absorption in the small intestine.
Further the walls of the intestine are rendered with blood vessels they deliver absorbed food to all cells of the body. The food that is digested is absorbed into the blood vessels in the walls of the intestine. The small intestine is the main site for the digestion of chyme and absorption of the nutrients from the digested material.
Any undigested or unabsorbed material left in the small intestine is passed here. An image of a simplified structure of the villus. All carbohydrates are absorbed as these.
The elimination of undigested residue from the body. The blood in the small intestine is filtered through the glomerulus before blood vessels transport the nutrients to other tissues. Absorption of Monosaccharides Amino Acids Dipeptides Tripeptides Lipids Electrolytes Vitamins and Water Glucose amino acids fats and vitamins are absorbed in the small intestine via the action of hormones and electrolytes.
These finger-like projections are specialized for absorption as they increase the surface area to absorb. Learning Objectives Describe the process of absorption of nutrients in the small intestine Key Takeaways Key Points. From the enterocyte linoleic acid glucose and amino acids enter the bloodstream while vitamin A and vitamin E pass into the lymphatic system.
The inner lining of the small intestine is richly supplied with villi. Question 26 1 pts Which statement best describes the absorption of nutrients. The blood carries the absorbed food material to different parts of the body.
What are the 4 mechanisms of nutrient absorption in the small intestine. The finger-like projections known as villi drastically increase the surface area of the small intestine for greater absorption of the digested food. From the cells of the small intestine glucose and vitamin C enter the bloodstream while EPA and vitamin A enter the lymphatic system.
The uptake of nutrients into the epithelial cells of the small intestine is a protein digesting enzyme A. Substances are taken up from the GI tract and enter the bloodstream or the lymph.
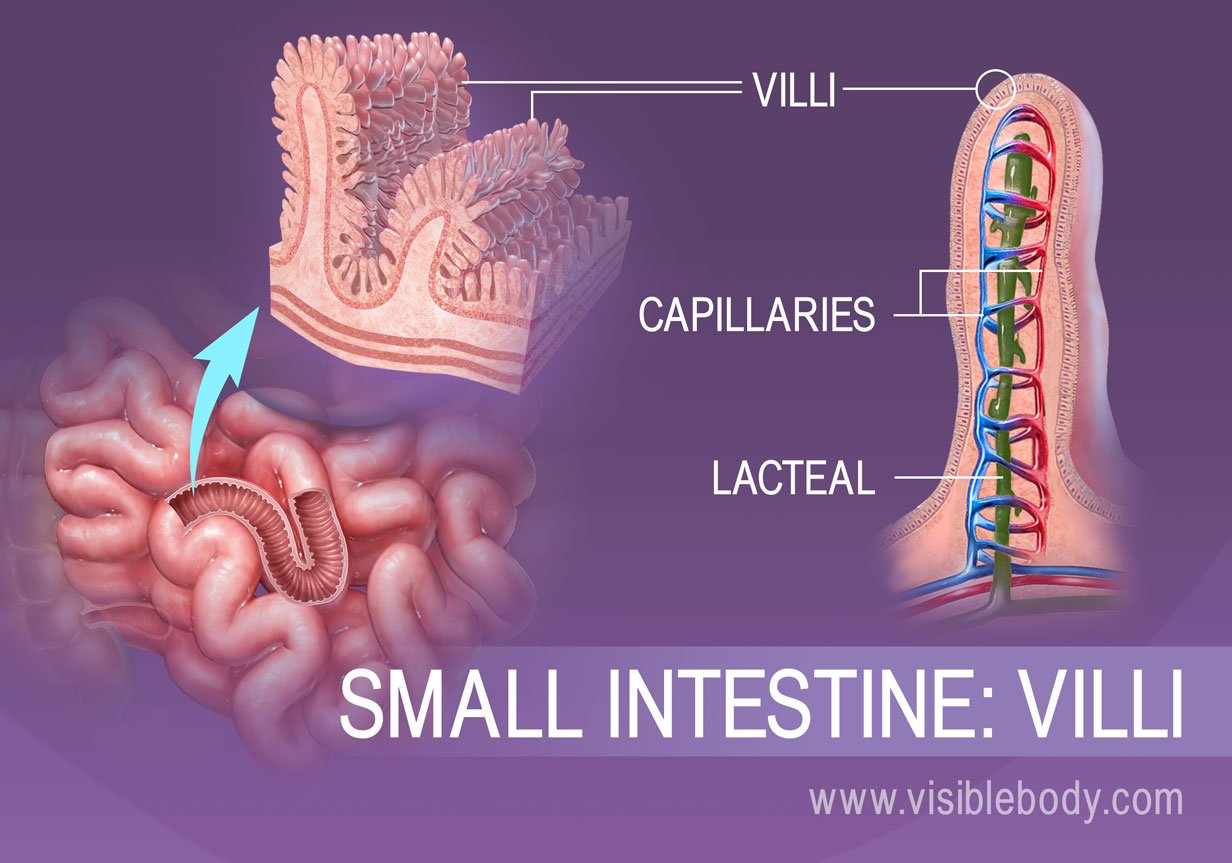
Absorption And Elimination Digestive Anatomy


0 Response to "Which Best Describes Absorption in the Small Intestine"
Post a Comment